There are four major blood groups: A, B, AB, or O. Blood types are differentiated by the types of antigens on the blood cells. Antigens are proteins on the surface of blood cells that can cause a response from the immune system. The Rh factor is simply a type of protein on the surface of red blood cells. Those who have the Rh factor are regarded as Rh-positive and those who do not have the Rh factor are Rh-negative. Rh senstization is considered to be a serious issue during pregnancy which require attention.
As part of the prenatal care checkup, a blood test will be conducted to find out the blood type. If the blood lacks the Rh antigen, it is called Rh-negative and if it has the antigen, it is called Rh-positive. When the mother lacks Rh antigen (Rh-negative) and the father possess Rh antigen (Rh-positive), the fetus can inherit the Rh factor from the father which makes the fetus Rh-positive. Problems may arise when the fetus’s blood has the Rh factor and the mother’s blood does not have Rh factor.
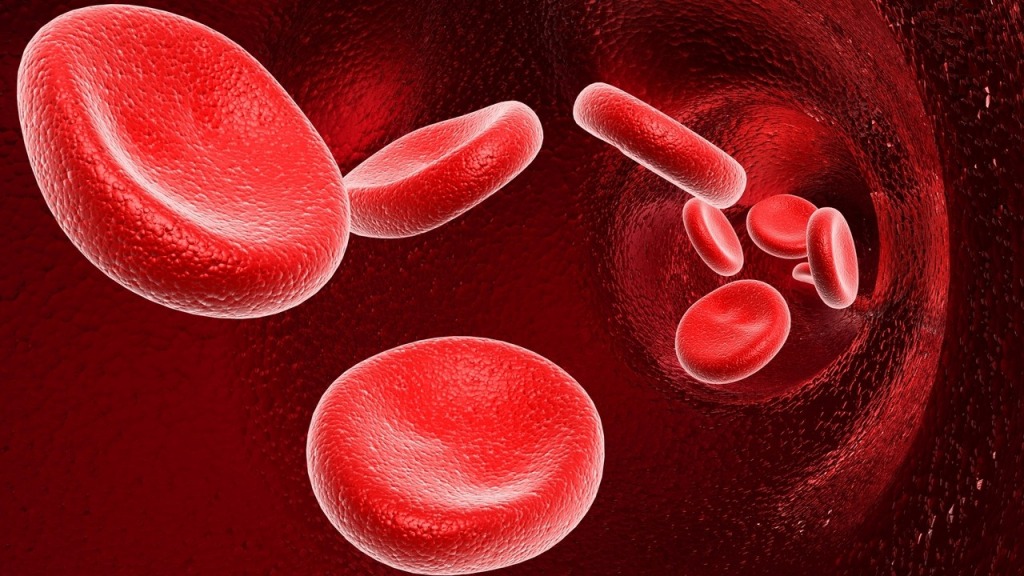
If you are Rh-negative, you may develop antibodies to an Rh-positive baby. Even if a small amount of the baby’s blood gets mixed with your blood, the body may respond allergically towards the baby. The mother’s body may make antibodies to the Rh antigens in the baby’s blood and these antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the baby’s blood.
This in turn break down the fetus’s red blood cells causing anaemia. This condition is referred as hemolytic disease or hemolytic anemia which may often lead to serious illness, brain damage, or even death in the fetus or newborn. Sensitization can occur at any time when the fetus’s blood mixes with the mother’s blood.
This may happen when the Rh-negative woman has had:

RhIg can be used even during pregnancy and after delivery:
An Rh-negative mother may receive RhIg after a birth, even if she decides to have her fallopian tubes tied or cut in order to prevent future pregnancies for the following reasons:
Once antibodies are developed, RhIg treatment does not help. A mother who is Rh sensitized must be regularly checked during her pregnancy period to see whether the fetus is developing the condition. The baby may be delivered on time, which can be followed by a blood transfusion in order to replace the diseased blood cells with the healthy blood. In severe cases, the baby may be delivered early and give transfusions from the mother’s uterus itself.
It is the most powerful creation to have life growing inside of you.There is no bigger gift